
To achieve the expected effect of removing pollutant particles from compressed air, it is essential to design and select the filtration equipment correctly.
Core Principles of Filter Selection
1. Precision Selection: “Choose What is Suitable”
The primary rule of precision is to match the filter to the specific requirements of the end-user.
Avoid Over-filtration: Exceeding accuracy requirements increases purchase costs, shortens service life, and creates higher pressure drops, leading to significantly higher operating costs.
The Trend: Higher filter accuracy generally results in higher initial costs and greater resistance in the process.
2. Capacity Selection: The 20% Rule
Filter capacity must be selected based on the air flow that needs processing.
Set a Margin: Always set aside a capacity margin of 20% to 30%.
Prevent Aging: Long-term full-load use causes filters to age prematurely, leading to decreased accuracy and increased pressure drops.
3. Layout and Sequencing
Proper arrangement ensures both air quality and equipment longevity.
Sequential Order: Filters should be arranged from low to high filtration accuracy.
Equipment Protection: Adsorption dryers require an oil removal filter at the front end and a dust filter at the back end.
The Series Myth: Using two identical filters in series does not double efficiency; particles that penetrate the first will likely penetrate the second, while resistance increases exponentially.
| System Type | Dew Point / Water Quality | Solid Particle Size | Residual Oil Content | Typical Applications |
| 1. Single-Stage | Liquid water present; 100% RH | 5μm | 5mg/m3 | Heavy machinery, cleaning, general workshop air |
| 2. Two-Stage | Liquid water removed; 100% RH | 0.01μm | 0.1mg/m3 | Food/beverage processing, pneumatic components |
| 3. Two-Stage + Refrigerated | 35.6∘F to 50∘F Dew Point | 0.01μm | 0.1mg/m3 | Spraying, sandblasting, textile machinery |
| 4. Three-Stage + Refrigerated | 35.6∘F to 50∘F Dew Point | 0.01μm | 0.03mg/m3 | Breathing gas, clean rooms, pharmaceuticals |
| 5. Three-Stage + Adsorption | Below −4∘F Dew Point | 1μm | 0.1mg/m3 | Electronics, air bearings, control instruments |
| 6. Sterilization + Refrigerated | Below 60% RH | 1μm | 0.1mg/m3 | Bioengineering, brewing, dental instruments |
| 7. Ultra-Clean System | Below −40∘F Dew Point | 0.01μm | 0.003mg/m3 | High-purity pharmaceutical & food processing |
7 Typical Filtration & Purification Systems
System 1: Single-Stage (General Purpose)
The most common method for general workshop air.
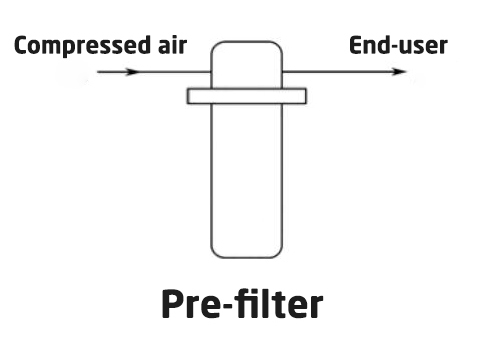
Best For: Heavy machinery, blow-cleaning, and general workshop use.
Quality: 5μm solid particles; 5mg/m³ oil; 100% relative humidity.
System 2: Two-Stage (Enhanced Protection)
Adds a fine filter to improve accuracy and protect the equipment life.
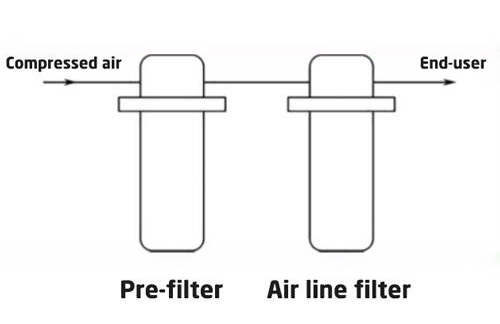
Best For: Air stirring, food/beverage processing, and general pneumatic components.
Quality: 0.01μm solid particles; 0.1mg/m³ oil.
System 3: Two-Stage with Refrigerated Drying
Includes a refrigerated dryer to freeze and separate water vapor.

Best For: Precision spraying, sandblasting, and textile machinery.
Quality: 35.6 – 50 ℉ dew point; 0.01μm particles
System 4: Three-Stage with Refrigerated Drying (Odor Removal)
Adds an activated carbon stage to remove oil vapors and smells.
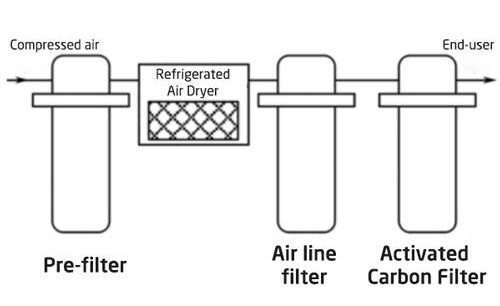
Best For: Breathing gas, pharmaceuticals, and clean rooms.
Quality: Odorless; 0.003mg/m³ residual oil.
System 5: Three-Stage with Adsorption Drying (Deep Dry)
Uses an adsorption dryer for applications requiring very low moisture.
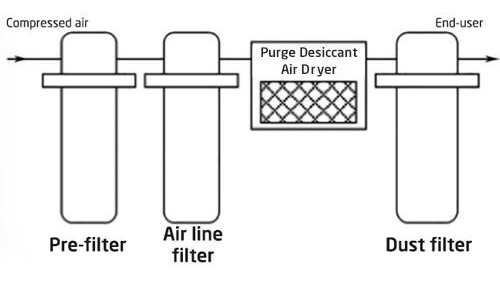
Best For: Control instruments, electronics, and air bearings.
Quality: Dew point below -4 ℉; 1μm solid particles.
System 6: Sterilization & Deodorization
A specialized system for removing bacteria and odors.
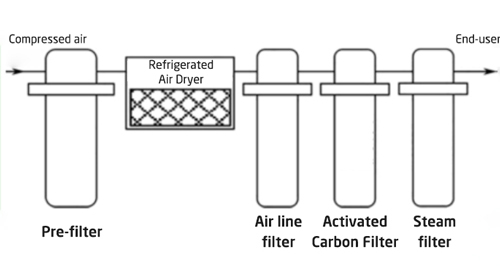
Best For: Bioengineering, brewing, and dental instruments.
Quality: Sterile and odorless; <60% relative humidity.
System 7: Ultra-Clean System
The highest level of purification for oil-injected air compressor systems.
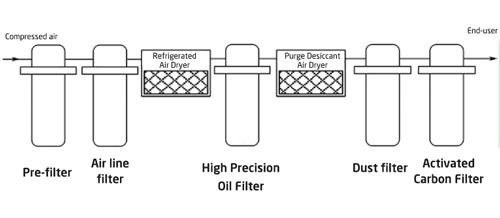
Best For: High-purity pharmaceutical and bioengineering applications.
Quality: Dew point below -40 ℉; 0.003mg/m³ oil; ultra-high cleanliness.
Conclusion
Choosing the right and appropriate air filter requires flexibility based on specific circumstances, while also considering cost-effectiveness.









-66x66.png)


