
With the global push for energy conservation and emission reduction, more and more companies are exploring new strategies to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
For example, the use of energy-efficient light bulbs and automatic heating equipment can effectively reduce carbon emissions, lower energy consumption, which is not only an environmentally friendly measure but also a way to alleviate the financial burden on businesses. In addition, waste heat recovery from air compressors is one of the important methods in the manufacturing industry to reduce their carbon footprint.
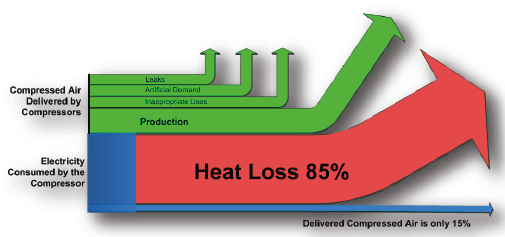
During the process of compressing air, a significant amount of thermal energy is generated because more air molecules are being squeezed into the same space. This thermal energy can be recovered and utilized. Generally, the compressed air involves two cooling stages, one during the compression phase itself and the other after compression is completed. The cooler removes the heat from the compressed air through air, water or oil, and this heat is transferred to the cooling medium through the heat exchange system.
The specific level of heat recovery may vary depending on the type of system. For example, air cooled systems are widely used in small to medium sized air compressors. They use low-pressure air flows to cool the compressed air, and this recovered heat can be used for heating buildings. The oil cooling system takes away the heat in the compressed air through the flowing oil, and this heat can be transferred to the production process through the heat exchanger. Water-cooling systems use circulating water to remove heat from compressed air, reducing external energy requirements by transferring heat to the manufacturing process.
The practical cases show that through waste heat recovery from air compressors, companies can significantly reduce carbon emissions and operational costs. For example, a UK automotive textile manufacturer, by using oil coolants to recover heat at the outlet of their air compressors, is able to reduce annual carbon dioxide emissions by 260,000 tons, saving 37,000 tons of carbon dioxide. Furthermore, a packaging factory in Northern Ireland uses its surplus heat to supply a local secondary school’s heating system, resulting in annual savings of £40,000 in heating costs and a reduction of 200 metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions.
Despite the significant potential of waste heat recovery from compressed air, its industrial application is not yet widespread. It is estimated that 90% of industrial air compressors can have heat recovery systems installed, allowing the recovery of 70% to 94% of the energy. According to calculations, if this technology were universally adopted, it could save 1.99% of the total electricity consumption in British industry, which is equivalent to eliminating the emissions of 913,000 diesel/gasoline cars annually or meeting the power needs of 1.544 million households each year. Therefore, waste heat recovery from compressed air is undoubtedly an excellent measure that not only saves costs but also aligns with energy conservation and emission reduction requirements.
Contact Us
If you need to purchase an air compressor with a heat exchanger, we have products that can meet your specific requirements.
Contact[email protected]Whatsapp+86 13501890887
Based in
No. 668. Delixi Road. Nanxiang Industrial Development Zone, Shanghai, PRC.
Contact[email protected]
Whatsapp+86 13501890887
Based in
No. 668. Delixi Road. Nanxiang Industrial Development Zone, Shanghai, PRC.









-66x66.png)



